Below are a few pictures with a brief description that will help you identify your car's sensors and let you know what they do:
- IAT Sensor: (inlet air temperature sensor)

Location:
IAT sensors are fitted to the Smart 599cc and 698cc engines instead of a MASS or MAF sensor. This sensor measures the temperature of the air entering the engine. Cold air is more dense, requiring more fuel. Warm air is not as dense as cold so requiring less fuel. The ECU takes readings from this sensor and compensate for changes in air temperature to maintain an almost perfect air-fuel mixture ratio.
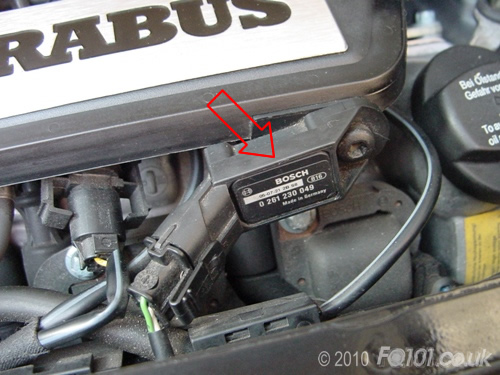
- MAP sensor: (manifold absolute pressure sensor)

Location:
This sensor measures the inlet manifold pressure and applies the right amount of fuel with the correct ignition timing so the car runs and performs properly, MAP sensor and the air temp sensor work together for the ECU knows how much fuel the mix with the air. If this sensor goes faulty the car will run it run badly, you will get poor fuel economy, lack of power and may sometimes get occasional stalling.
- Lambda Sensor: (oxygen sensor)

The lambda sensor measures oxygen content information and sends it to the ECU. The ECU then makes minor second by second adjustments to the fuel and air ratio being used by the engine. This ensures that gases are burnt efficiently by the catalytic converter. If the lambda sensor becomes faulty, the engine management system sends a default amount of fuel to the chamber and activates the engine warning light.
- Coolant temperature sensor

Location:
This sensor reads the coolant temperature from the top of the thermostat housing, this is a sender unit which alot of people get confused with a switch.
As it is a sender its only job is to relay the temperature to the cars ECU, it is also responsible for temp display on the speedo.
- Fuel level sensor

The fuel level sensor is actually combined in a complete replacement fuel delivery unit, This makes things quite expensive as it contains the fuel pump as well as the sensor, this whole unit is screwed into the top of the fuel tank which requires the whole tank to be dropped in order to replace.
It may sound obvious but if this unit fails then your fuel gauge will not function correctly.
- RPM sensor

This sensor bolts on the top of the gearbox and counts the rotation of the engine. It supplies the management system and the dash RPM gauge with RPM values.
- Gear position sensor

This sensor bolts on the side of the gearbox to inform the ECU which gear the car is currently in. If this sensor fails the car will flag up the error by displaying three bars on the dash and the car will remain immobile.
- Yaw sensor (mk4- mk6)

This sensor picks up the lateral acceleration of the car (sideways movement) as part of the Trust+ system in order to cut power under hard cornering. If this part fails the 'Trust' lamp may illuminate on the dash board and some (if not all) of your traction control systems will not function. This sensor is only found present in cars fitted with Trust+.
- Lateral acceleration sensor (mk7+)

Location (Roadster):
Location (fortwo 450):
This sensor is a more advanced version of the above, It works alongside the steering angle sensor to calculate the lateral acceleration against turning angle. This is part of the 'ESP' system and instead of just cutting the power it manages it through the corner. If this part fails the 'ESP' lamp may illuminate on the dash board and some (if not all) of your traction control systems will not function.
- Crankshaft position sensor TDC

The TDC sensor sits on the top of the bell housing to calculate the position of the crankshaft, it reads engine speed and allows the management system to change injector openings with changes in engine rpm.
- Wheel speed sensor (ABS)

The wheel speed sensor does just that; it calculates the speed in which the wheel is spinning and sends the information to the cars management system to control the ABS system. It looks for the wheel's speed or if the wheel locks under braking to decide the appropriate action. A faulty speed sensor will cause the ABS not to function correctly and may illuminate the ABS lamp on the dash.
One of the smart's weak points is the reluctor rings corrode and need replacing giving the same symptoms as a faulty sensor.
- Knock sensor
This sensor sits on the back of the engine up against the firewall and listens for pinking (pre detonation). It contains a piezoelectric sensor that listens for knock by detecting pressure, the signal is the converted into voltage and sent to the ECU.
If this sensor fails some of the symptoms you should expect are the car feeling sluggish, poor fuel economy and poor acceleration. This is caused by the ECU reducing the ignition timing to the engine as a response to false readings from the sensor.
- External air temperature sensor
As well as displaying external air temperature on your dash, the temperature sensor is also used to control the heater booster (on diesel models) and manage the ABS in icy conditions. This communication usually occurs when the external temperature drops below 3 degrees centigrade and the snowflake symbol illuminates on the dash. The sensor is located in different positions depending on your car.
Roadster: Located under the left rear panel next to the air intake: